How is a collaborative meeting opened?
Many of my business colleagues are curious: How do you conduct a collaborative meeting yourself in your organization? In order to solve this problem, we have written this article to share the current "Collaboration Conference" assisted by the PDIS team.
Many corporate colleagues are curious: How do you conduct a collaborative meeting yourself in your organization? In order to solve this problem, we have written this article to share the process of the "Collaboration Conference" assisted by the current PDIS team.
Why do you need a collaborative meeting?
The past meeting format, there are several common problems. First of all, the moderator is often a senior official, although professional, but may be labeled as one of the parties, resulting in the neutrality of the meeting was questioned. In terms of meeting members, it may be limited by existing connections, contacts, and actively developing multi-stakeholders related to the issue; for example, sometimes there may be many alternatives to the issue, but not necessarily at the beginning. think. When there is a lack of alternatives and corresponding stakeholders, different solutions or corresponding views on the issue are difficult to present.
In the course of the meeting, because of the bureaucratic structure of the public service system, some civil servants at the grassroots level did not dare to say the implementation problems, which caused the problems to be unrepresented. At the stage of the meeting, many meetings even found new feasible Solution, but because the organizers are not sure how to coordinate with the stakeholders again, it is difficult to change the general direction, and can only adjust the details. Even if you hear more opinions, it is difficult to find the key issues again. In terms of the form of the meeting, it is often the way to talk about each other. After each statement, the moderator will show that there is no opportunity to focus on the issues discussed by you, and there is no opportunity to clarify the thoughts of everyone.
How do collaborative meetings solve these problems? First, the collaborative meeting is organized and organized by the PDIS team moderators to organize and organize the issues. On the one hand, it helps to examine the information and discussions provided by the department from a third party perspective. The two aspects are not only unilateral in the meeting. The parties will also be asked to add their opinions and clarify the disputes as a buffer between the parties and the ministry.
Before the meeting, in addition to the inventory issues, PDIS will also count the relevant stakeholders, so that the meeting can cover as many voices as possible, and let everyone's opinions be added as much as possible.
In the inventory of interested parties, first of all, issues related to the topic, such as front-line personnel related to the issue, service providers, relevant scholars and experts, or organizations concerned with this issue, etc. Open the possibility of thinking about multi-stakeholders, and let the ministry be limited by existing connections and connections.
Moreover, the content details of the topic may also have different impact levels, or you need to explore alternatives that can achieve the same purpose. From here, you can also find different stakeholders to think about different solutions. Finally, we should also review whether we are concerned with all stakeholders and whether they have enough knowledge and experience to represent the corresponding types of stakeholders. For example, is the representative of the scholar familiar with this topic and can provide sufficient information? Whether the representative of the relevant group can provide the troubles of the corresponding stakeholders, rather than the case experience and so on.
With the inventory of stakeholders, it is possible to solve the problem of being limited by existing connections and contacts, and therefore unable to think and think.
In the way of meeting, the current collaborative meeting is mainly about 5 hours. In the morning, we will first invite different stakeholders to report their understanding and suggestions on the topic, and add the content to the topic. The mind map also invites them to supplement the context in which the mind map is still lacking. In the afternoon, we will think about and clarify the more feasible solutions, try to find out the possible specific solutions, and identify the risks and major authorities that may be encountered.
In addition to the on-site comments or paintings on the post-it notes with the verbal instructions, and then add the ideas to the mind map according to the corresponding context, and also open the scene and the remote participants, using Sli.do the online (anonymous) questioning tool assists in collecting opinions. the mental map uses realtimeboard digital whiteboard to assist in organizing comments, and the finishing method is also included in KJ. Method and ORID focus discussion method. In the afternoon, various design methods will be used to assist in thinking. It will also be incorporated into the concept of a standing meeting, so that everyone can have an organic discussion in an active atmosphere and record the concept of feasibility. As the atmosphere is alive, everyone can also have their own organic discussions, as well as third-party hosting, to avoid problems that are difficult to focus in past meetings, and to allow colleagues in different locations to speak their own observations.
As for the past meetings, because the government has a draft, it is difficult to change. On the one hand, through the focus of different stakeholders at the meeting, everyone can have a consensus on "why change" at a time, instead of having to Once again, the objects of different roles will gather consensus and reduce the corresponding burden. In addition, before the policy is produced, the imagination of different stakeholders can be confirmed first, and the situation of the draft policy can be avoided.
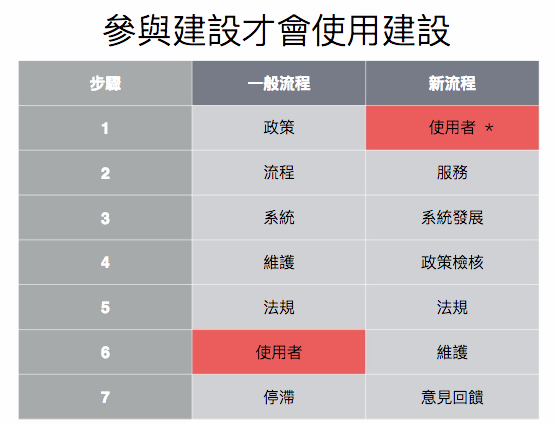
What should I do before the collaborative meeting is held?
Before the collaborative meeting is held, it is necessary to collect and sort out various materials related to the issue through the topic analysis form. Through the issue analysis form, the department will be more likely to understand how to prepare for the event and record the content. The content of the issue analysis table includes the various issues related to the proposal and the issues related to the issue, the context behind the issue, the stakeholder inventory, the feasibility and solution of the existing and future co-organizers, and the collection of evidence. The
claims are intended to clarify the "problems" and "proposal solutions" of the proposers and the second parties to ensure that the follow-up discussions are focused and to find specific solutions. After
, there will be several pre-conference meetings. This meeting will mainly help the various ministries to divide and focus on the content of the topic. Many of the problems are actually problems that the government has not encountered in the past. Naturally, there are not necessarily precedents to follow. Under this circumstance, the windows of each ministry will take stock of these businesses, including the current policies that have been implemented, the division of labor, and whether there are corresponding research reports in the past.
In this process, with the information of the parties, you can gradually count the situation that appears in the problem. According to the maturity of the issue, if the topical ministry has already been counted, it will also promote the policy of the ministry in the pre-conference meeting and make preliminary thoughts.
This side needs to digest and understand the connotation of the party's questions first, and then roughly divide the issue into several major directions, and then contact the sponsor. When you contact, you need to try to ask the real reason behind the party's problem. For example, in [Hengchun Case] (https://realtimeboard.com/app/board/o9J_k0G2Vcg=/), the party thinks that the problem of "the current delivery is not fast enough" should use the "air force corps stationed at Hengchun Airport." This solution is handled, but the actual cause of the problem is actually "the lack of local medical resources in Hengchun", so it will result in "the current delivery is not fast enough". It is an important step to clarify the core issue. After inquiring about the reasons behind the parties' problems, you can try to ask the parties to propose the solutions they imagined. First, record the solutions, and the future can be used as a reference for internal research.
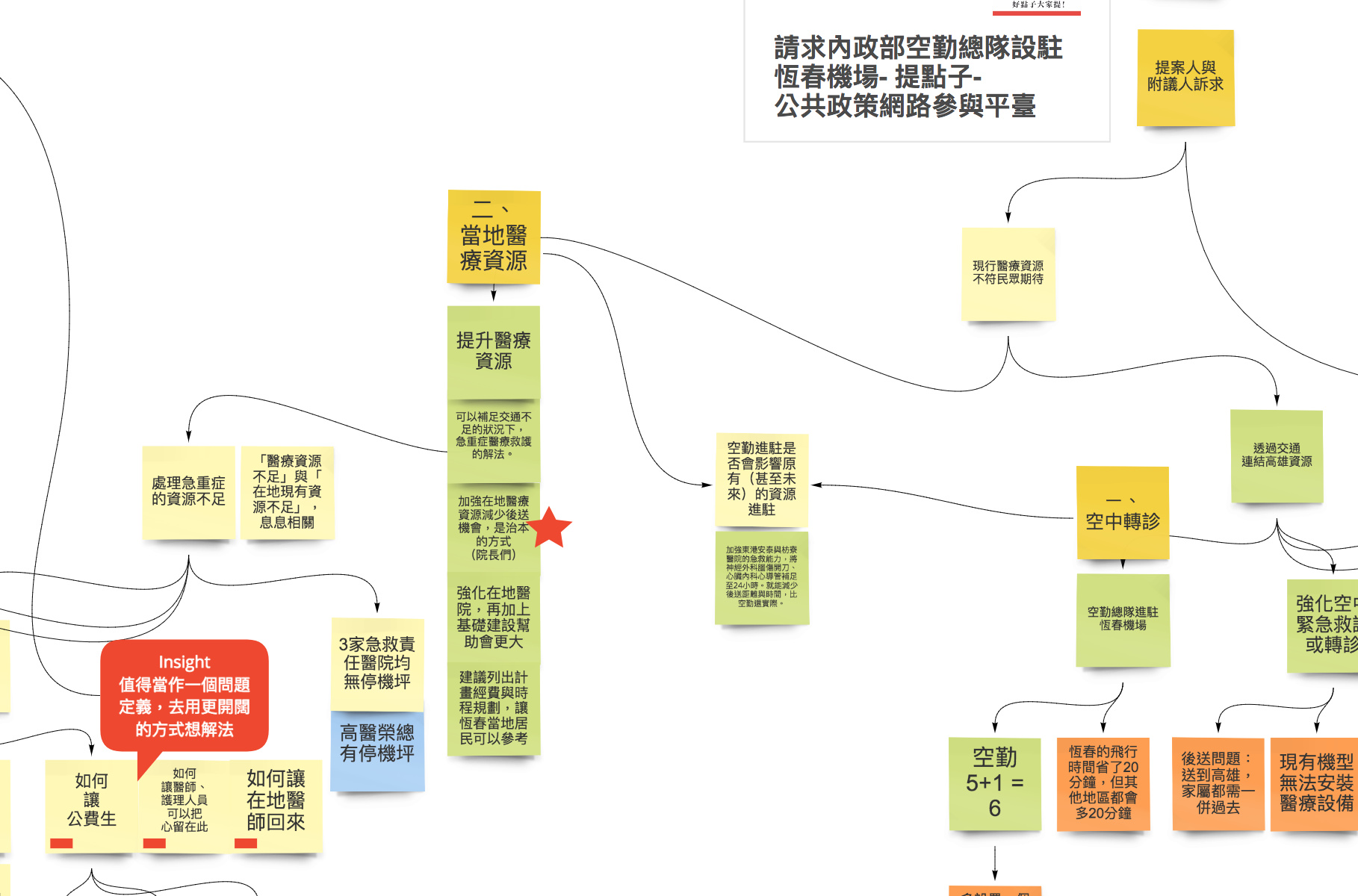
Next, we will also sort out the opinions from each pipeline. For example, the propaganda people on the Join platform will leave a message to make suggestions. They can be different from the Liaison's appeals, but they still get a lot of people's support for the message, as the attached information, and the current issues related to this issue, And the solution recommended by the sponsors and netizens is written to expand the relevant reasons and solutions for this problem.
Next, for these reasons, the main responsibilities and co-organizers can work together to sort out the current policies and treatment guidelines, as well as the position of the ministry. Some people may worry that the position of the ministry will be criticized, but in fact it is impossible for someone to really have no position. In fact, the self-declaration position can help everyone understand each other and make the discussion progress more smoothly.
After then, you can collect relevant information on these problems and solutions, including relevant news reports, scholars' discussions, and even papers. After all, many problems may actually be a preliminary experience. If relevant information is used as evidence, it can confirm whether it is an objective fact. At the same time, there are many corresponding analytical materials and methods behind the news reports and discussions, which can be used as an important reference for thinking. data.
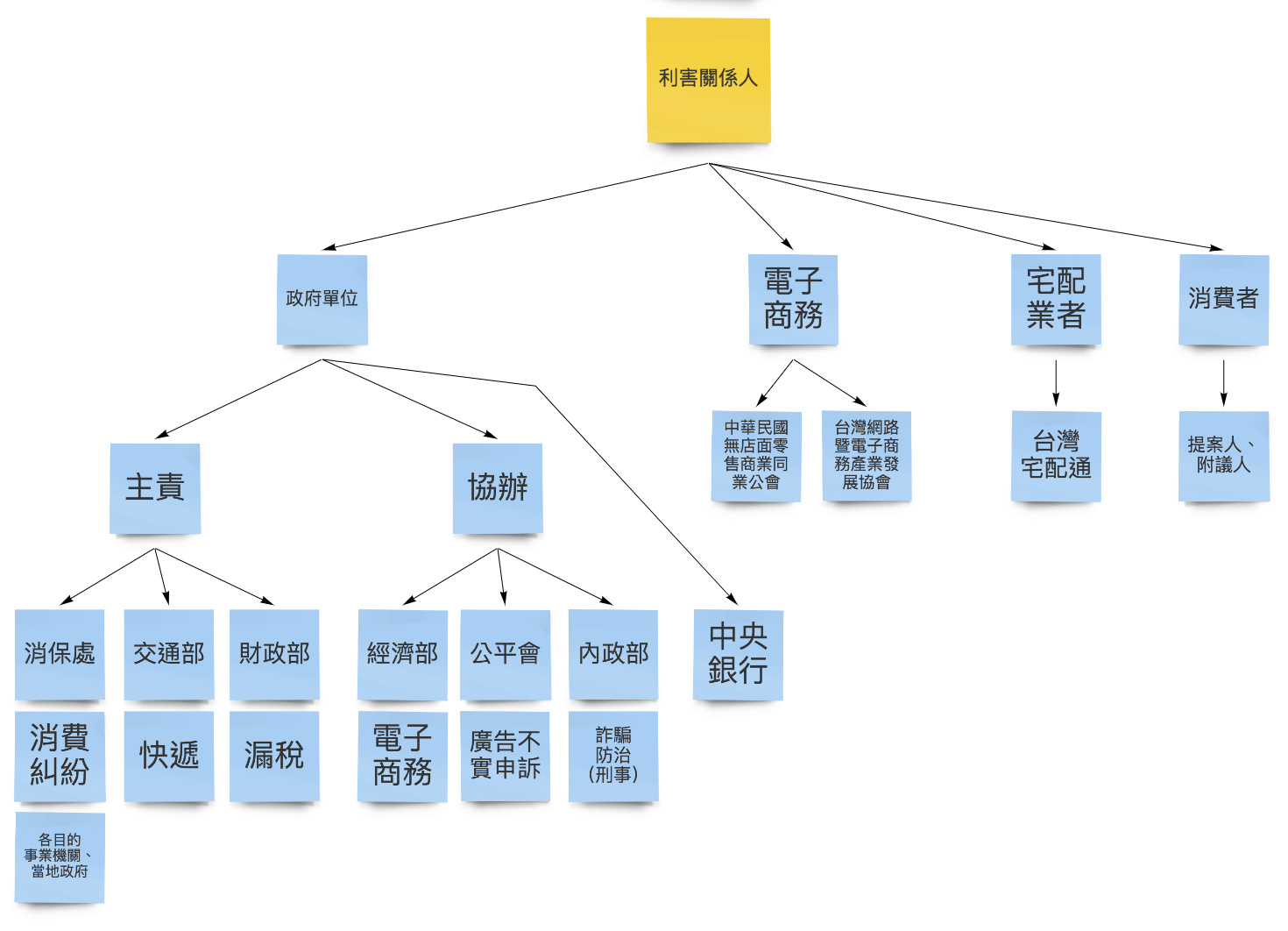
Finally, it's about the stakeholder. There is a need to ask the sponsors to provide groups, vendors, people, etc. related to the issue. The sponsoring authority also needs to list the stakeholders and fill in the associations between the participants and the issues. It should also be noted here that sometimes the sponsor may be a unilateral stakeholder, and the issue may have other stakeholders with different positions, such as the problem of locomotive road rights. Other users may also be interested parties. Such as trucks, taxis, etc. If you are not invited to come together, there may be no more comprehensive discussion of the issue. After all, some questions will be understood by the real parties.
After the problem is sorted out, the moderator (projectconsultantZhangFangrui) will spend time reading the materials, looking for reference materials, and sorting the above questions into the structure of the mind map.
This mind map has several directions. One is to count the stakeholders and the mental maps of the relevant ministries. This mental map will organize the ministries related to the issue and the related businesses they are responsible for; stakeholders will also write their relevant positions to help you clarify the relationship between these stakeholders and issues.
In terms of issues, we will first sort out the topics, divide the issues into several levels, problem classification, related issues, suggested solutions, government responses, related restrictions, and supplements with background information. It is important to note that we need to be careful about the level of opinion. Sometimes it is a problem to solve the problem. For example, "requiring "quick review" is the suggested solution, not a problem; sometimes it is necessary to explore the reasons behind the problem more carefully, to avoid the final analysis being built on the wrong Imagine it.
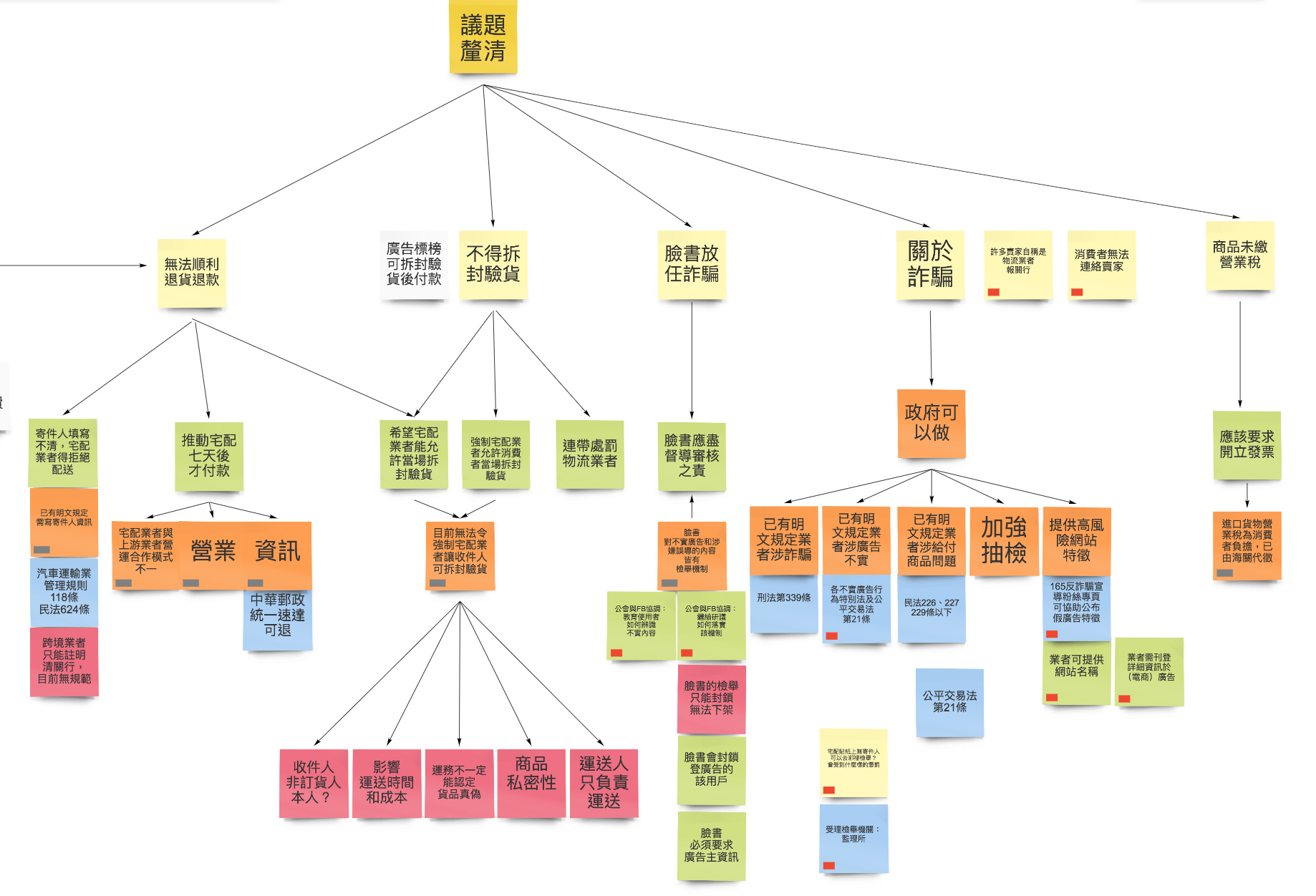
Sometimes these issue ministries have already implemented corresponding policies, and will ask the ministry to supplement their current practices and solutions so that the sponsors can understand the current policies and will be more discussed in the future. Can focus on the parts that have not been properly handled yet.
Of course, if you want to analyze the issue more completely, it is best to collect relevant papers, interview the interested parties, organize their views, and define the corresponding nouns. Thread and political will. With a consistent definition, the meeting has the basis for discussion. After the information is ready, you can hold a collaborative meeting.
Collaborative Meeting Process
At the beginning of the collaborative meeting, the host will introduce the process and implementation of the entire meeting to ensure that everyone can understand the content and procedures discussed in the meeting; The limits of this meeting, for example, under the current mechanism, the conclusion will inform the dean and the relevant ministry, but will not produce an administratively effective final decision on the spot, nor will it be binding, to avoid false expectations of the meeting.
Next is a report from the ministry and stakeholders to ensure that everyone at the venue can understand the context of the issue. After the report, the two parties will be invited to work together to post the opinions on the issue analysis mental map that are still missing, and supplement the opinions on the mind map. After arranging the post-it notes, the person who wrote the post-it notes should go to the front and post a comment on the post-it notes to express their opinions.
After filling the mind map, it is usually time to eat at noon. After the meal, there will be a few key issues to be selected in the afternoon. Through the concept development sheet, everyone will analyze the fundamental problems behind the problem and the small improvement that the government can make first under the current regulations. After the discussion, the friends who participated in the meeting were also invited to take the stage to report possible solutions.
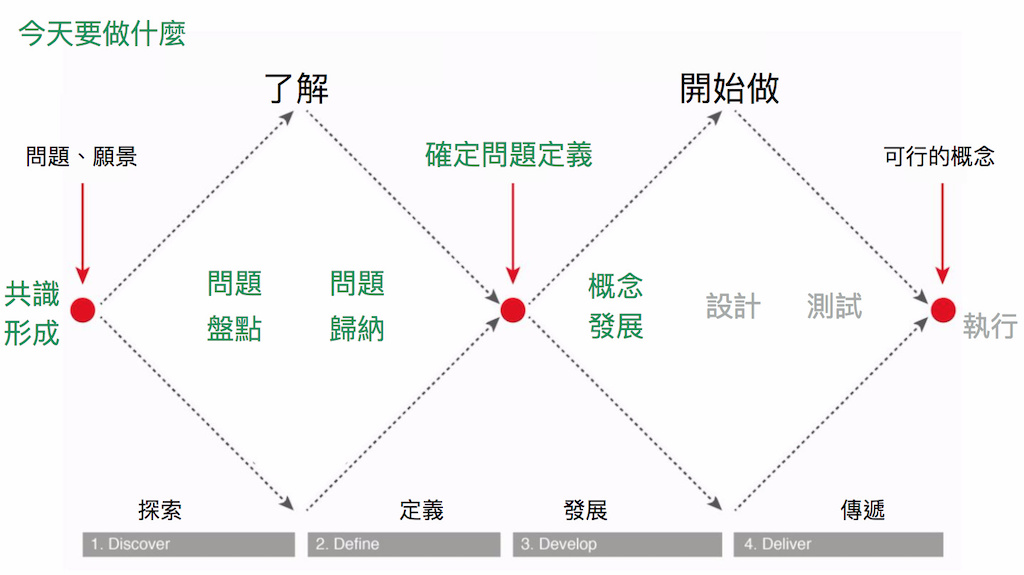
The final conclusion will also be explained again. The results of this meeting will be reported to the Dean and relevant government council members at the government meeting next week, so that they can understand the context of the issue and let relevant government agencies promote relevant in the future. You can participate in the policy.
In the follow-up process, at the monthly open government meeting, open government liaisons need to report the progress of the issue until the case has been initially implemented.
Currently, the PDIS team has produced the tools and concepts of the collaborative conference as "PO101", and you are welcome to refer.
Future Challenges
Currently, in specific cases (eg reporting software case), the people can go further and participate in later collaboration through similar mechanisms. But how do you expand to more proposals? This requires the collaborative process to be embedded back into the existing administrative process.
For example, if a collaborative meeting requires political empowerment, how do you get such an authorization so that the results of the collaborative meeting can be accepted? Is there a way for a collaborative meeting to accommodate more people and more opinions? If there is a legal amendment, when it is necessary to go to the Legislative Yuan, how can the results of the discussion be used by the legislators, or let the legislators attend the meeting from the beginning to provide their opinions and opinions?
These are still the challenges that collaborative meetings will need to address in the future.
Taiwan is a democratic society. Political figures have their own channels and methods for collecting opinions. Government units also have a stable policy development process. How can the open government process be embedded so that the policy can be shaped more fully and with more comments? It is a topic that we must continue to face.
 (This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.)
(This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.)